|
|
| What is ZigBee? |
|
| |
|
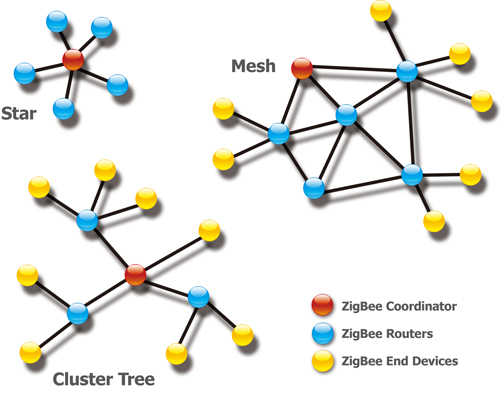
ZigBee is a specification based on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard for wireless personal area networks (WPANs). ZigBee operates in the ISM radio bands, and it defines a general-purpose, inexpensive, self-organizing, mesh network for industrial control, medical data collection, smoke and intruder warning, building automation and home automation, etc. There are three different types of ZigBee devices in a ZigBee network:
There are three different types of ZigBee devices in a ZigBee network:
- Full function device – ZigBee Coordinator (Master):
Only one coordinator exists in each ZigBee network. Its function is to store information about the network and to determine the optimum transmission path between any two nodes of the network.
- Full function device – ZigBee Router (Slave):
Router acts as an intermediate node that always in the active mode. Its main function is to transfer and pass the data among the devices.
- Reduced Function Device – ZigBee End Device (Slave):
This device contains a minimal amount of functionality to enable it to talk to its parent node (either the coordinator or a router); it is normaly in sleep mode and cannot relay data directly from other devices.
There are three topologies defined in the ZigBee standard: Mesh, Star and Cluster Tree. |
|
 |
|
| |
|
ZigBee network uses a basic master-slave configuration that is suited to the dynamic mesh networks of many infrequently used devices that talk via small data packets. Up to 256 nodes are allowed. |
|
| |
|
ZigBee VS Bluetooth
ZigBee wireless communication is focused on control and automation, while Bluetooth is focused on connectivity between laptops, PDA’s, and the like, as well as more general cable replacement. ZigBee uses low data rate and a low power consumption, and works with small packet devices; Bluetooth uses a higher data rate and a higher power consumption, and works with large packet devices. Compared to Bluetooth, ZigBee networks can support a larger number of devices and allows a longer range between devices. |
|
| |
|
ZigBee VS SST-2450 Wireless Modem
SST-2450 wireless modem is used for middle distance wireless applications. In addition to the simple half-duplex communication, it is particularly suitable for the peer-to-peer full-duplex communication networks. Compared to the wireless modem, ZigBee supports various ad-hoc network topologies, such as mesh, star and cluster tree. It also supports repeater functionality in redundancy systems. |
|
| |
|
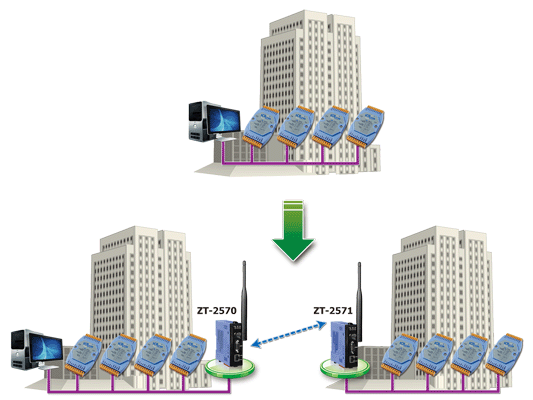
About ZT-2570/ZT-2571 Converter
ZT-2570/ZT-2571 is a set of Ethernet/RS-485/RS-232 to ZigBee Network converter. It enables Ethernet/RS-232 /RS-485 devices to be wirelessly and easily connected to a new or existing system.
ZT-2570 and ZT-2571 support various data formats and Baud Rates that can be configured via a Windows-based GUI utility. In a ZigBee network, ZT-2570 is the net-host (Coordinator) and ZT-2571 is the net-slave (Router). The ZT-2570/ZT-2571 can implement a mesh, star or cluster tree network topology.
In some existing systems that use an Ethernet/RS-485/RS-232 network, it is sometimes difficult to extend the new devices due to building structure issues, wiring problems or other reasons. The ZT-2570/ZT-2571 can be easily added to an existing system in order to extend your network. |
|
| |
|
About ZT-2550/ZT-2551 Converter
ZT-2550/ZT-2551 is a set of RS-485/RS-232 to ZigBee Network converter. It enables RS-232/RS-485 devices to be wirelessly and easily connected to a new or existing system.
ZT-2550 and ZT-2551 support various data formats and Baud Rates that can be configured via a Windows-based GUI utility. In a ZigBee network, ZT-2550 is the net-host (Coordinator) and ZT-2551 is the net-slave (Router). The ZT-2550/ZT-2551 can implement a mesh, star or cluster tree network topology.
In some existing systems that use a RS-485/RS-232 network, it is sometimes difficult to extend the new devices due to building structure issues, wiring problems or other reasons. The ZT-2550/ZT-2551 can be easily added to an existing system in order to extend your network. |
|
 |
|
| |
|
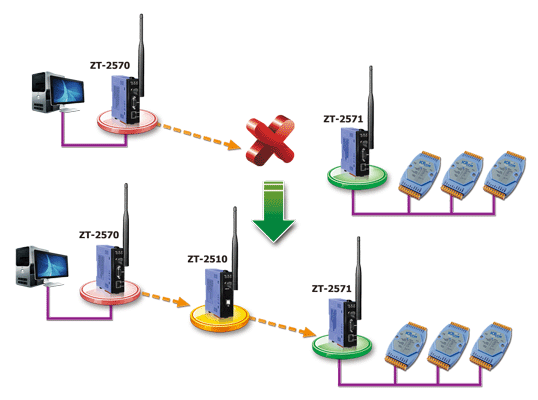
Using ZT-2510 as a Repeater
For advanced wireless applications, using repeaters to implement a mesh topology is required in order to build a more flexible and reliable network. The ZT-2510 repeater can be used to avoid an obstacle that may be located between two wireless devices or to extend the wireless transmission range. |
|
 |
|
 |
|
| |
|
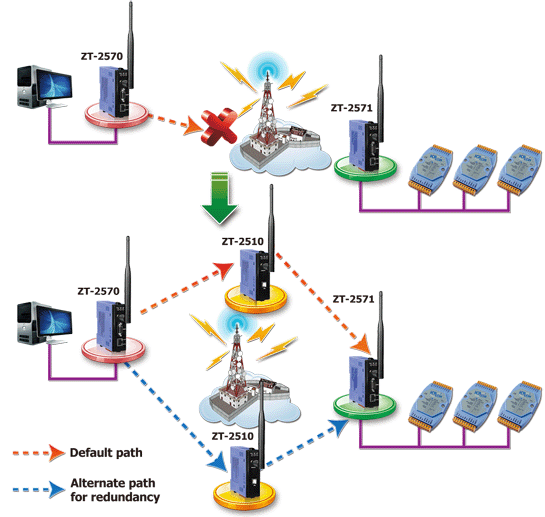
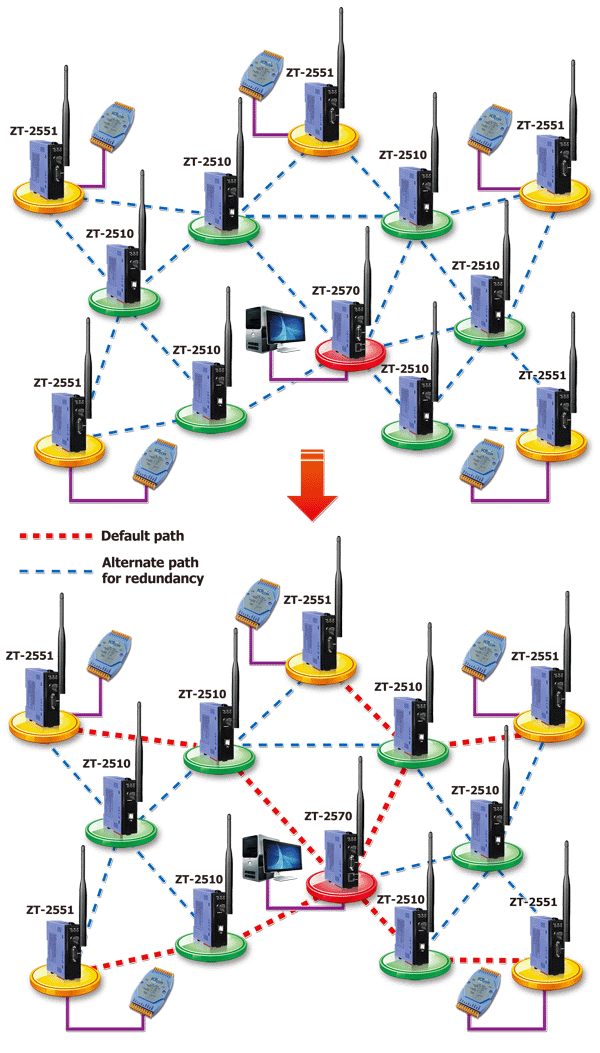
Using ZT-2570, ZT-2571 & ZT-2510 to implement a Mesh Network
Wireless transmission is greatly affected by humidity, temperature, weather, obstacles, electromagnetic interference, etc. It is very difficult to exclude, especially in industrial environments. However, the mesh topology, the most important feature of the ZigBee wireless transmission, exactly can overcome or avoid such kind of interferences.
The benefits of using a mesh topology are shown below:
- When mesh network discovers a new node, it will automatically incorporate it into the current network.
- If a node in bad communication, the mesh network will route the data through an alternate path using another node.
- Adding additional repeater nodes to your network enables each node to have more possible paths for transmission. It also allows a redundancy to be incorporated into the system in a much simpler way than with other types of system.
|
|
 |
|
| |
|
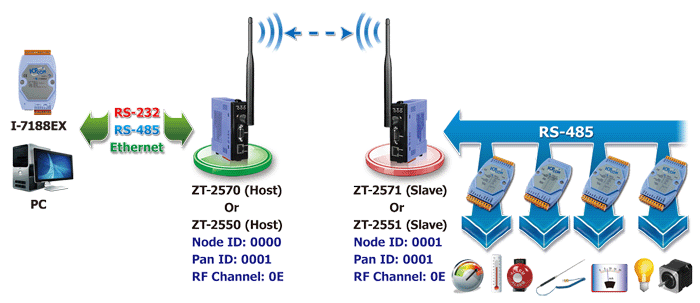
ZT-2570 & ZT-2571 with ICP DAS 7000 Series
P2P: peer to peer |
|
 |
|
| |
|
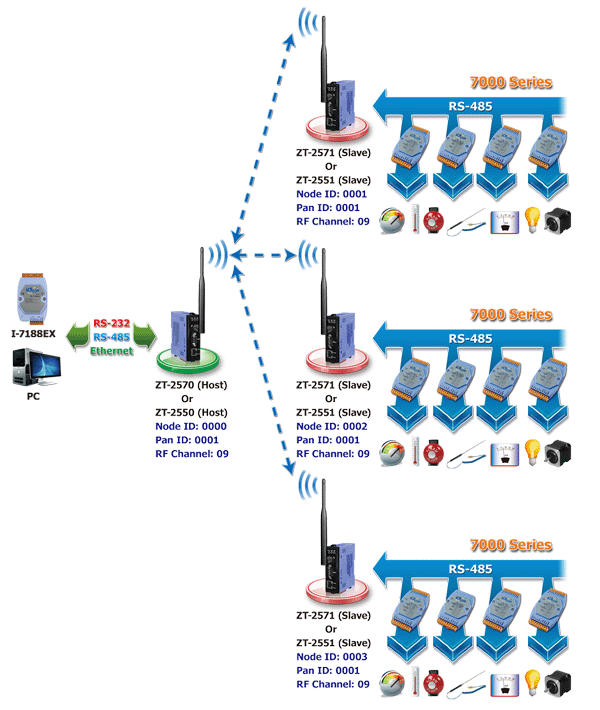
P2M: peer to multi-peer |
|
 |
|
| |
|
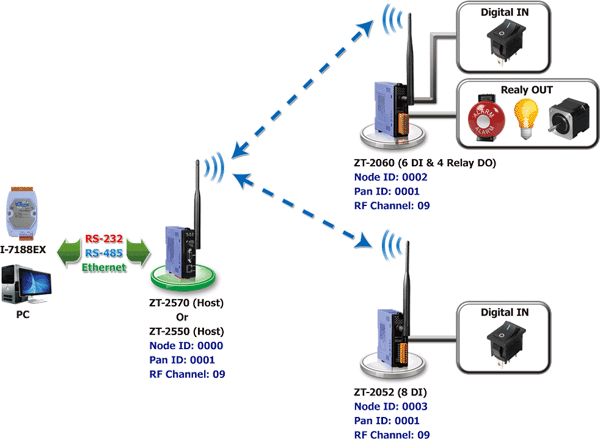
ZT-2570 with ICP DAS ZT-2000 Series
|
|
| |
|
 |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| TOP |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|