|
|
|
 |
|
N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
|
|
|
 |
|
|
| N |
| - NTSC |
| The National Television
System Committee is most notably responsible for developing the analog
television standard currently in use throughout the U.S., Canada, Japan
and 31 other countries, worldwide. The NTSC system standard stipulates
a 60Hz vertical refresh rate, refreshed in alternating even and odd
fields. Furthermore, the lines of the even and odd fields are
vertically offset from one another; ensuring that the lines of the odd
fields falls between the lines of the even field (interlacing). Each
frame consists of one odd, and one even field, and is broadcast at 525
horizontal lines of resolution (only 487 lines are visible, due to
vertical refresh synchronizing). The typical description of NTSC
standard is defined by image resolution 640 (H) x 480 (V) pixels, and
frame rates of 30 frames per second/60 fields per second. |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| O |
| - Optical
Magnification |
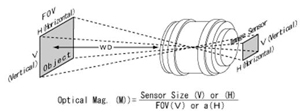
| Magnification is
the process of enlarging something only in appearance, not physical
size. Magnification is also a number describing by which factor an
object was magnified. In some fields, this number may be less than one,
corresponding to an apparent reduction in size. This is sometimes
called Minification. Optical Magnification is the ratio between the
apparent size of an object
(or its size in an image) and its true size. The Magnification ratio is
indicated by the symbol "X". A 10X are enlarging ten times object
apparent. |
 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
| P |
| - PAL |
| The television broadcast
standard throughout the majority of Europe, Australia, Mainland China,
and 45 other countries worldwide, is the PAL standard. The PAL standard
utilizes a 50 Hz vertical refresh rate, refreshed in alternating even
and odd fields. Each frame consists of one odd, and one even field, and
is broadcast at 625 horizontal lines of resolution (only 580 lines are
visible, due to vertical refresh synchronizing). The typical
description of PAL standard is image resolution around 768 (H) x 576 (V)
pixels and frame rate can up to 25 frames per second/50 fields per
second. |
| |
|
| |
| - Pincushion
Distortion |
| Pincushion
distortion is a lens effect, which causes images to be pinched at their
center. Pincushion distortion is associated with telephoto lenses, and
typically occurs on the camera side of a zoom lens. The use of converters often amplifies the
effect. It is most visible in images with non-perfectly straight lines,
especially when they are close to the edge of the image frame. |
 |
|
| |
|
|
| |
| - Pixel Clock |
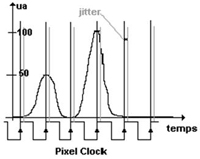
| The pixel clock
divides the incoming horizontal line of video into pixels. This pixel
clock has to be stable, relative to the incoming video or the picture
will not be stored correctly. The higher the frequency of the pixel
clock, the more pixels that will appear across the screen (pixel
resolution). |
 |
|
| |
|
 |
| - Pixel Size |
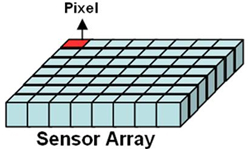
| Most CCD and CMOS
imagers consist of picture elements dubbed "pixels". Each pixel is one
sensor within the array and has a definite size, which should be
available by the manufacturer. Sizes typically range from 8-20 microns.
The pixel size is a technical parameter that relates to resolution,
process feature dimensions and pixel architecture. For a given die
size, a high resolution requires a small pixel. |
 |
|
| |
|
| |
| |
| - Progressive-scan |
| A system of video
scanning whereby lines of a picture are transmitted consecutively, such
as in the computer world. This method is often
used in DVD video encoding where the video is produced by scanning the
film. It is also used in enhanced and high definition television
systems as it is supposed to produce less visual artifacts than the
interlaced mode but requires a higher refreshing rate. |
 |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
| R |
| - RGB vs. CMYK |
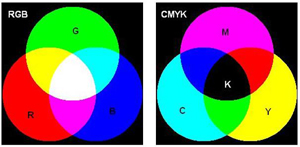
| RGB (Red, Green, and Blue) - The basic components of color television
system. They are also the primary colors of light. CMYK (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and black) - This is a color space primarily
used in color printing The CMYK color space is subtractive, meaning
that cyan, magenta, yellow and black pigments or inks are applied to a
white surface to remove color information from the white surface to
create the final color. |
| |
 |
| |
|
| |
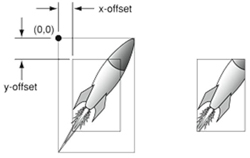
| - ROI |
| ROI is means the
region of interest. A user-defined, rectangular area (a square is
common) on a CCD that is exposed and processed as an image. For image
processing field, the ROI also means a user-defined area for inspection
or measurement application for saving system images processing time.
Therefore sometime its also call “AOI, Area of
Interest”. |
 |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
| S |
| - Saturation |
| Saturation
describes the amount of color present in an image. Although commonly
mistaken, saturation does not refer to the brightness of a
color; simply the amount of pigment used to make the color. The less
pigment, the less saturated the color is. |
 |
| |
|
| |
| - SECAM |
| Sequential Couleur a
Memoire (French for Sequential Color with Memory) is the television
broadcast standard in Russia, France, the Middle East, and most of
Eastern Europe (worldwide total 29 countries). The SECAM system offers
the same resolution and update rate capabilities, as seen in the PAL
system, but SECAM provides for sequential color transmission and
storage in the receiver. |
|
| |
|
| |
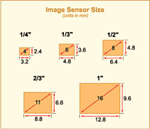
| - Sensor Size |
| The
“Sensor Size” is the dimensions of CCD/CMOS sensor
area, which is responsible for transforming light into electrical
signals. Typically, the sensor size from 1/4” to 1”
and measured by diagonal size. |
 |
|
| |
|
 |
| - Smear |
| During the CCD
readout phase, cells are shifted down on the entire area of the CCD.
While they are shifted, they continue to collect light. If the shifting
is not fast enough, errors can result from light that fall on a cell
that was not in its proper position. These errors are referred to as
"vertical smear" and cause a strong light source to create a vertical
line above and below its exact location. |
 |
|
| |
|
| |
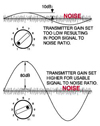
| - S/N Ratio |
| Signal to Noise
ratio; Parameter for measuring quality of signals in dB (Decibel
units). The higher the ratio is, the better the quality of the signal. |
 |
|
| |
|
| |
| - Sobel
Transform |
| The Sobel Transform
is an edge detection technique based in gray scale gradients in
vertical, horizontal, and diagonal directions. Each pixel in a
transformed image has an intensity that represents the intensity
gradient present at it’s location in the image. |
 |
|
| |
|
 |
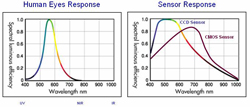
| - Spectral
response |
| Generally, the
human eyes can accept the light wavelength range from 400 nm to 700 nm
and it is called “Visible light”. The light
intensity under 400 nm is call “UV (Ultraviolet)
light” and wavelength range from 800 nm to 900 nm is call
“Near infrared light”,
and when over 1000 nm is call “Infrared light”. Due
production characteristics, the CCD sensor can respond to light, with
wavelengths ranging from 400 nm to 1000 nm. By working together, the CMOS
and CCD sensor, can register light from 400 to 1000 nm. |
 |
|
| |
|
| |
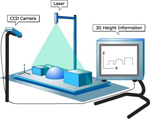
| - Structured
Light |
| Structured Light is
use of patterned lighting to help determine shape of three-dimensional
objects. The pattern may be static or changing with time. Fanned out
laser beams, scanning laser beams, and projected patterns are used. |
 |
|
| |
|
| |
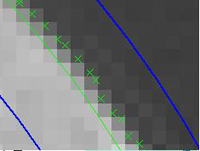
| - Sub Pixel
Resolution |
| Sub Pixel
Resolution is the ability to make measurements finer than the pixel
resolution. It comes in two varieties, statistical and
gray scale. Together they can allow measurement resolution as good as
1/50th the length of the acquired pixels. An example of statistical sub
pixel resolution is the 2D calculation of the centroid (center of
gravity) of a circular disk shape. The calculated center is based on a
floating-point average of all points in the disk as recognized by
binary thresholding of the image. |
 |
|
| |
|
 |
| - S-Video |
| S-Video is a
hardware standard that defines the physical cable jacks. The comb
filter separates the color information (C, Chrominance) and luminance
information (Y) of a video signal into separate parts. This is also
called Y/C, where Y represents brightness and C color. |
 |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| T |
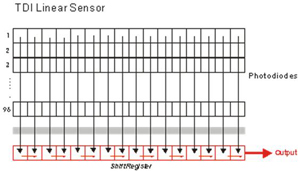
| - TDI
Line-scan Camera |
| TDI (Timing Delay
Integration) - This unique CCD structure consists of 96 rows of
photodiodes that accumulate light detected from a single exposure. The
accumulated light is converted to an electric charge signal, and sent
to a single output. Because the accumulated luminance is greater than
that of typical line-scan cameras, TDI cameras are best suited for
settings with low light availability. TDI cameras are highly dependent
on consistent sampling rate and motion speed. If the motion speed is
unstable, images will become blurry. |
 |
| |
|
| |
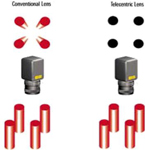
| - Tele-centric
Lens |
| The optical unit
within the camera assembly uses Tele-centricity to ensure that
board-warping, stationary distance, and position within the field of
view, does not affect the alignment accuracy. Alternately, cameras can
get the same surface image through Tele-centric Lens. |
 |
|
| |
|
 |
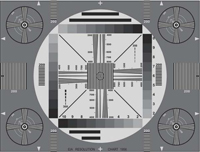
| - TVL |
| As a unit of
measurement for resolution, "television lines" or TVL refers to the
maximum number of alternating black dots and intervening white spaces
that can occur and be distinguished in a straight line whose length is
equal to the diameter of the largest circle that fits in the screen or
other area of reference. Typical test pattern is use “EIA
Resolution Chart 1956” for measurement cameras resolution. |
 |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| W |
| - White Balance |
| Normally our eyes
compensate for lighting conditions with specific color temperatures.
With a digital camera, the camera needs to find a reference point,
which represents the color white. It will then calculate all the other
colors based on this reference point.
For instance, if a halogen light illuminates a white wall, the wall
will have a yellow cast, while in fact it should be white. Therefore,
if the camera knows the wall is supposed to be white, it will then
adjust all of the other colors in the scene accordingly. |
 |
| |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|